The English language is brimming with words that may seem simple yet pose significant challenges to both native speakers and learners. Among these words, “like” and “as” are frequently confused.
They are both used to compare things, but their grammatical functions and the nuances they convey are distinct.
Understanding how to use them correctly can enhance clarity and precision in communication, making interactions more effective and reducing misunderstandings.
Recognizing the differences between “like” and “as” is particularly helpful for writers, students, and anyone who wishes to master English grammar.
By learning to differentiate between these two words, one can improve both spoken and written English, ensuring that comparisons are accurate and the intended meanings are conveyed.
This knowledge is essential for producing clear, concise, and grammatically correct sentences, whether in academic writing, professional correspondence, or casual conversation. ️
In this article, we will explore the differences between “like” and “as,” their grammatical roles, and how to use them properly.
We will delve into detailed explanations, provide illustrative examples, and highlight common mistakes to avoid.
By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of how to use “like” and “as” effectively, enhancing your overall communication skills. Let’s dive into the nuances of these two commonly confused words and unravel the rules that govern their usage.
You might also enjoy: Top 100 Commonly Used Verbs That Start With A [2024]
Differences Between “Like” and “As”
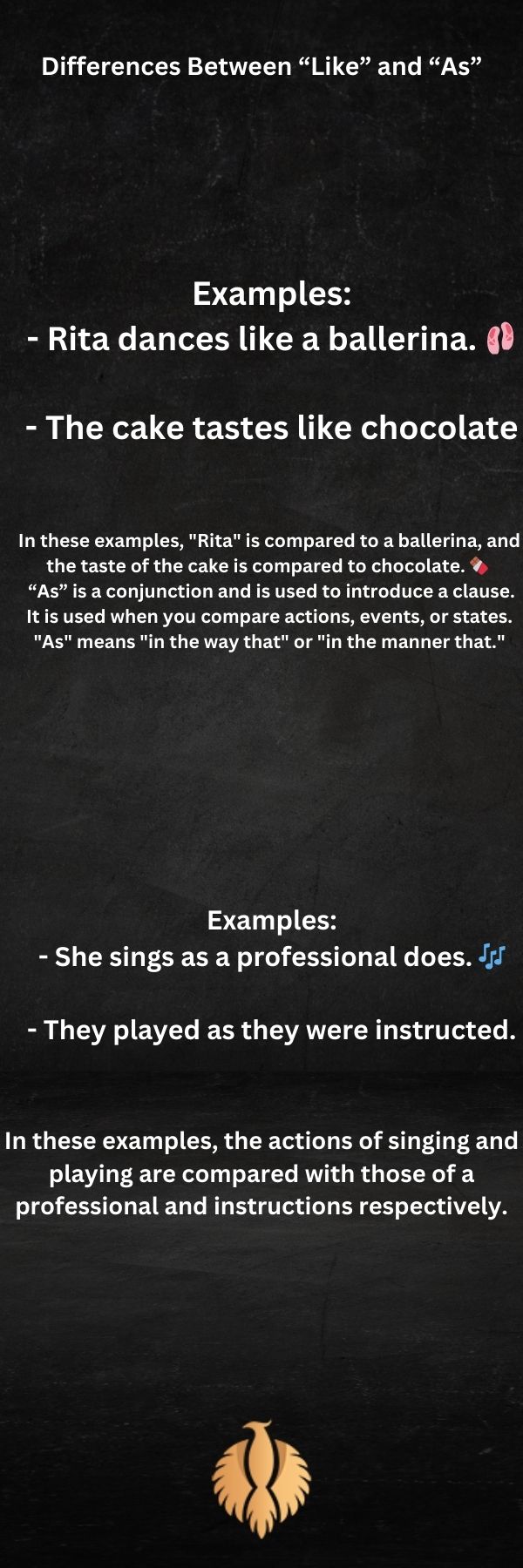
“Like” is a preposition and is commonly used to compare nouns and pronouns. It denotes similarity or likeness. When you use “like,” you compare a subject with a noun or pronoun. “Like” means “similar to” or “in the same way as.”
Examples:
– Rita dances like a ballerina.
– The cake tastes like chocolate.
In these examples, “Rita” is compared to a ballerina, and the taste of the cake is compared to chocolate.
“As” is a conjunction and is used to introduce a clause. It is used when you compare actions, events, or states. “As” means “in the way that” or “in the manner that.”
Examples:
– She sings as a professional does.
– They played as they were instructed.
In these examples, the actions of singing and playing are compared with those of a professional and instructions respectively.
Grammatical Roles of “Like” and “As”
Like :
1. Preposition: “Like” is primarily used as a preposition. It is followed by a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase.
– Example: Lucas swims like a fish.
2. Similes: “Like” is often used in similes to draw a comparison.
– Example: Sophia’s smile is like sunshine. ☀️
As :
1. Conjunction: “As” functions as a conjunction and introduces a clause.
– Example: He acts as if he owns the place.
2. Comparative Conjunction: “As” is used to compare two clauses.
– Example: She can sing as beautifully as her sister.
3. Roles and Functions: “As” can denote roles or functions.
– Example: Emma works as a teacher.
You might also enjoy: Paid Vs Payed : Differences + Examples [My 2024 Teaching Way]
Detailed Examples and Contexts
To further elucidate the differences between “like” and “as,” let’s consider some unique examples with distinctive names and contexts.
Like as a Preposition:
1. Amir runs like a cheetah.
– Here, Amir’s speed is compared to that of a cheetah.
2. Nina designs clothes like a fashion designer.
– Nina’s design skills are compared to those of a fashion designer.
Like in Similes:
1. Sina’s voice is like music to my ears.
– The pleasing nature of her voice is compared to music.
2. His handwriting is like a chicken scratch.
– The messy nature of his handwriting is compared to chicken scratch.
As as a Conjunction:
1. David played the guitar as if he were a rock star. ⭐️
– David’s manner of playing the guitar is compared to that of a rock star.
2. Mia painted the mural as she had envisioned it.
– Mia’s action of painting the mural is compared to her vision.
You might also enjoy:Which of the Following: Definition + Complete Usage + Grammar
As in Comparative Conjunctions:

1. Lucy is as tall as her brother.
– Lucy’s height is compared to her brother’s.
2. They can run as fast as a gazelle.
– Their running speed is compared to that of a gazelle.
As Denoting Roles:
1. Jake works as a consultant.
– Jake’s role is a consultant.
2. Sophia serves as the team leader.
– Sophia’s function is that of a team leader.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Despite their clear functions, “like” and “as” are often misused. Here you see common mistakes and how to avoid them:
1. Using “like” instead of “as” :
– Incorrect: She sings like she is a professional.
– Correct: She sings as if she were a professional.
Tip: Remember, “as” is used to introduce clauses and compare actions or states.
2. Using “as” instead of “like” :
– Incorrect: He swims as a fish. ♀️
– Correct: He swims like a fish.
Tip: “Like” is used for direct comparisons with nouns or pronouns.
You might also enjoy:To Bad Or Too Bad – Correct Grammar + Examples [2024]
Advanced Uses and Nuances
As in Idiomatic Expressions:
– As far as This phrase means “to the extent or degree.”
– Example: As far as I know, he is reliable.
– As soon as: This phrase means “immediately at the moment that.”
– Example: Call me as soon as you arrive.
Like in Informal Speech:
– In informal conversation, “like” is often used as a filler part.
– Example: Like, I was just thinking, you know?
Like to Express Preference:
– Like can also indicate preference or habitual actions.
– Example: I like to read in the evenings.
As in Phrasal Verbs:
– Phrasal verbs using “as” often indicate roles or states.
– Example: They took him as he was.
You might also enjoy: Cancelled or Canceled; Spelling; Examples [2025]
Practice Exercises

To solidify your understanding of “like” and “as,” try these practice exercises:
1. Fill in the blanks with “like” or “as”:
– She speaks ______ a native speaker.
– He fought ______ a lion in the ring.
– They danced ______ gracefully ______ professional dancers.
2. Identify the errors and correct them:
– He sings like he was on Broadway.
– She acted as a child when she didn’t get her way.
Answers:
1. as, like, as … as
2. He sings as if he were on Broadway. She acted like a child when she didn’t get her way.
Understanding the distinct roles of “like” and “as” not only enhances grammatical precision but also enriches the quality of expression.
These words, though seemingly small, have a substantial impact on the clarity and meaning of our sentences.
By mastering their usage, you can communicate more effectively and with greater finesse.
You might also enjoy:Boys’ or Boy’s– Which One is Correct? + Example
Conclusion
Mastering the use of “like” and “as” is crucial for effective communication in English. These two words, though seemingly simple, play distinct roles in comparing objects, actions, and states.
“Like,” functioning as a preposition, is used to draw direct comparisons between nouns and pronouns.
On the other hand, “as,” functioning as a conjunction, is used to introduce clauses and compare actions or states in a more complex manner.
Understanding these differences enhances clarity and precision in both written and spoken communication.
It helps avoid common grammatical errors and ensures that comparisons are accurate and meaningful.
This knowledge is particularly beneficial for writers, students, and language learners who aim to articulate their thoughts clearly and effectively.
By recognizing the unique roles of “like” and “as,” you can construct sentences that convey your intended message with finesse.
Whether you’re crafting a literary piece, composing an email, or engaging in everyday conversation, a firm grasp of these words will enrich your linguistic skills and elevate your communication.
So next time you find yourself choosing between “like” and “as,” remember their specific functions and let them guide you in expressing your thoughts with precision and clarity.

Hi, welcome to my blog! My name is Omid and I am thrilled to have you here! I am an English language teacher with 12 years of experience and hold multiple international certifications (TESOL, IELTS, TOEFL, PTE, CELTA). Additionally, I hold a PhD in Applied Linguistics with a specialization in Teaching English as a Second Language (TESL), which fuels my passion for teaching English and assisting others in mastering the language. To me, nothing is more rewarding than helping individuals enhance their English language abilities through various methods. So, let’s embark on this journey of learning English together.




