Language is a wonderfully intricate system, and within it, certain words can spark confusion due to their similarities in sound or spelling.
Three such terms often discussed in linguistic circles are homophones, homonyms, and homographs.
To directly address the title, here’s a comprehensive look at the differences between these three concepts along with examples to clarify their meanings and usage.
Definitions and Examples:
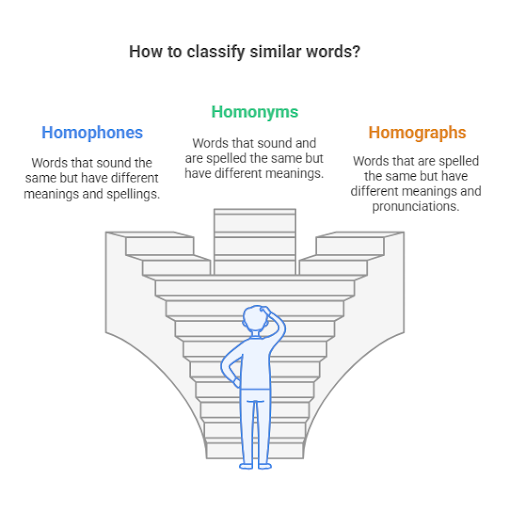
- Homophones: Homophones are words that sound the same but have different meanings and often different spellings. For example:
– Flour (the powder used in baking) and flower (the blooming part of a plant).
– Two (the number 2), to (a preposition), and too (meaning also).
- Homonyms: Homonyms can refer to two types of words: those that sound the same and are spelled the same (a specific type of homophone) and those that may be spelled differently but share the same pronunciation.
Most commonly, however, homonyms refer to words that have different meanings but are either pronounced or spelled the same. For example:
– Bat (an implement used in sports) and bat (a flying nocturnal animal).
– Bark (the sound a dog makes) and bark (the outer covering of a tree).
- Homographs: Homographs are words that are spelled the same but have different meanings and may or may not be pronounced the same. For example:
– Lead (to guide or direct) versus lead (a type of metal, pronounced “led”).
– Tear (to rip) versus tear (a drop of liquid from the eye).
You might also enjoy:Which of the Following: Definition + Complete Usage + Grammar
### Important Points:
- Sound vs. Spelling: Homophones are primarily concerned with how words sound, while homographs focus on spelling regardless of pronunciation. Homonyms can include aspects of both, as they may refer to words that sound the same and/or are spelled the same.
- Context Is Key: The meaning of these words often depends heavily on their context in a sentence. For example, the word “bark” can refer to either a sound made by a dog or the outer layer of a tree depending on how it is used.
- Usage in Communication: Understanding these differences is crucial for effective communication. Misusing homophones, homonyms, or homographs can lead to misunderstandings.
For instance, confusing “their” (possessive form of “they”) with “there” (a place) or “they’re” (a contraction of “they are”) can change the entire meaning of a sentence.
- Language Evolution: With the evolution of language, the meanings and common usages of words can shift. Familiarity with these terms can enhance clarity and precision in both spoken and written English.
In this discussion, we will explore homophones, homonyms, and homographs in greater detail, providing additional examples and contexts.
We aim to help you grasp these concepts effectively, allowing you to enhance your linguistic skills and avoid common confusions in everyday communication.
Ultimately, understanding the distinctions between homophones, homonyms, and homographs opens up a richer engagement with the English language.
By becoming familiar with these terms and how they function within our speech and writing, we empower ourselves to communicate more clearly, creatively, and accurately.
Let’s dive deeper into these fascinating aspects of language as we enhance our comprehension and proficiency in communication.
You Might Also Enjoy:Reinforce Vs Reenforce: 10 Differences + Examples [2025]
- Homophones
Homophones are words that share the same pronunciation but have different meanings and often different spellings.
The similarity in sound can create confusion, especially in spoken language. Examples of homophones include “bare” and “bear,” “flour” and “flower,” or “write” and “right.” Mastering homophones is essential for effective communication, as choosing the wrong word can lead to misunderstandings.
- Homonyms
Homonyms are words that share the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings. There are two types of homonyms:
- Homographs:These are words with the same spelling but different meanings. For instance, “lead” (to guide) and “lead” (a metal) or “tear” (to rip) and “tear” (a drop of liquid from the eye) are homographs.
- Homophones:As mentioned earlier, homophones are a subset of homonyms. They have the same pronunciation but different meanings, like “pair” and “pear,” or “peace” and “piece.”
Homonyms add layers of complexity to language, requiring careful consideration of context to discern the intended meaning.
You might also enjoy:Looking Forward To Seeing You: Grammar + Examples[2025]
- Homographs
Homographs specifically refer to words that share the same spelling but may have different pronunciations and meanings.
They can be a subset of homonyms, encompassing both homophonic and heterophonic pairs. Examples of homographs include “lead” (to guide) and “lead” (a metal), “row” (a disagreement) and “row” (a line), or “read” (past tense) and “read” (present tense).
Understanding homographs requires attention to both spelling and context, as the pronunciation often changes based on the intended meaning.
So we can say that,homophones, homonyms, and homographs enrich the English language with their intricacies.
Navigating these linguistic subtleties demands a combination of sound judgment, context awareness, and a keen eye for spelling. As language enthusiasts explore the interplay of these terms, they uncover the nuances that contribute to the depth and beauty of communication.
You might also enjoy:Where Does “How is your Day Going?” Originate From?
What is the difference between homophone and homonym?

The difference between homophones and homonyms lies in their specific characteristics related to pronunciation and meaning.
Homophones
Definition: Homophones are words that share the same pronunciation but have different meanings and often different spellings.
Example: “Two” and “to” are homophones. They sound the same but have distinct meanings and spellings.
Homonyms
Definition: Homonyms are words that share either the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings.
You might also enjoy:Interested In or On: The Differences + Examples [2025]
Two Types of Homonyms
- Homographs: These are words with the same spelling but different meanings and sometimes different pronunciations. Example: “Bow” (a knot) and “bow” (to bend forward).
- Homophones: A subset of homonyms, homophones have the same pronunciation but different meanings and often different spellings. Example: “Flower” and “flour” are homophones.
Summary
– Homophones focus on similar pronunciation, potentially leading to confusion in spoken language.
– Homonyms encompass both homophones and homographs, referring to words that share the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings.
Understanding the distinction between homophones and homonyms is essential for precise and effective communication, particularly when navigating the complexities of the English language.
You might also enjoy:What Kind of Vs What Kinds of – Differences + Examples [2025]
Summary about homograph
Homographs are words that share the same spelling but may have different meanings and, in some cases, different pronunciations. This linguistic phenomenon adds depth and complexity to the English language. There are two main types of homographs:
| 1. Homographs with Same Pronunciation (Homonyms):Words that share the same spelling and pronunciation but have different meanings. For example, “tear” (to rip) and “tear” (a drop of liquid from the eye) are homographs with the same pronunciation. |
| 2. Homographs with Different Pronunciations:These words have the same spelling but different meanings and are often pronounced differently. An example is “lead” (to guide) and “lead” (a metal), where the pronunciation changes based on the intended meaning. |
Navigating homographs requires careful attention to context and pronunciation, showcasing the linguistic richness that arises from words with shared spellings but diverse meanings.
What are homophones and homographs examples?
Here are examples of both homophones and homographs:
| Homophones: |
| 1. **Two / To / Too:** We have **two** options. Let’s go **to** the store. It’s **too** hot outside. |
| 2. **Flower / Flour:** She picked a beautiful **flower**. Use this **flour** to bake the bread. |
| 3. **Bear / Bare:** The large **bear** roamed the forest. Don’t go outside in your **bare** feet. |
| Homographs: |
| 1. **Lead (to guide) / Lead (a metal):** She will **lead** the team. The pencil is made of **lead.** |
| 2. **Tire (to exhaust) / Tire (a rubber covering for a wheel):** I don’t want to **tire** you out. Check the air pressure in the **tire.** |
| 3. **Bow (to bend forward) / Bow (a weapon or a decorative knot):** **Bow** down when you greet the queen. The gift was wrapped with a beautiful **bow.** |
These examples illustrate the distinctions in meaning for homophones and homographs, showcasing the intricacies of the English language.
You might also enjoy:Too Cute Meaning Vs To Cute (To Vs Too) + Examples
Here are 20 examples of homographs

- **Bass (a type of fish) / Bass (a low-pitched sound)**
- **Bow (to bend forward) / Bow (a weapon or a decorative knot)**
- **Close (to shut) / Close (near in distance)**
- **Content (satisfied) / Content (information in a book or website)**
- **Desert (a dry, arid region) / Desert (to abandon)**
- **Lead (to guide) / Lead (a metal)**
- **Object (a thing) / Object (to express disagreement)**
- **Permit (to allow) / Permit (an official document)**
- **Refuse (to decline) / Refuse (garbage)**
- **Tire (to exhaust) / Tire (a rubber covering for a wheel)**
- **Read (past tense) / Read (present tense)**
- **Tear (to rip) / Tear (a drop of liquid from the eye)**
- **Row (a line) / Row (a disagreement)**
- **Wound (an injury) / Wound (past tense of wind)**
- **Tire (to exhaust) / Tire (a rubber covering for a wheel)**
- **Lead (to guide) / Lead (a metal)**
- **Content (satisfied) / Content (information in a book or website)**
- **Minute (a unit of time) / Minute (very small)**
- **Polish (to make shiny) / Polish (from Poland)**
- **Rebel (to resist authority) / Rebel (a person who resists authority)**
These examples showcase words with the same spelling but different meanings and, in some cases, different pronunciations.
You might also enjoy:How Are You Fairing or Faring? Differences + Examples
Is Bow a homonym or homograph?
The word “bow” is both a homonym and a homograph.
-Homograph:”Bow” is a homograph because it has the same spelling but can have different meanings. For example, “She tied her shoes with a bow” (a decorative knot) and “The violinist played a beautiful bow” (a curved stroke made by a stringed instrument).
-Homonym: “Bow” is a homonym because it has different meanings while sharing the same spelling. It can refer to both a decorative knot and the curved stroke made by a stringed instrument, and these meanings are unrelated.
So, in the case of “bow,” it is both a homonym and a homograph.
Here are 15 examples of homonyms

- Bow:
– He tied his shoes with a bow.
– The violinist played a beautiful bow.
- Lead:
– She will lead the team to victory.
– The pencil is made of lead.
- Tire:
– Don’t tire yourself out.
– Check the air pressure in the tire.
- Bear:
– The bear roamed the forest.
– I can’t bear the thought of losing.
- Close:
– Close the door quietly.
– The store is too close to our house.
You might also enjoy:Emersion Vs Immersion: Meaning, Differences, and Examples
- Content:
– He is content with his life.
– The website provides informative content.
- Minute:
– Wait for a minute.
– Details are written in minute handwriting.
- Object:
– She has a new object for her collection.
– I object to the proposed plan.
- Permit:
– I will permit you to enter.
– Do you have a parking permit?
- Refuse:
– I refuse to do that task.
– Dispose of the refuse properly.
- Tear:
– Please don’t tear the paper.
– A tear rolled down her cheek.
- Wound:
– He suffered a wound in battle.
– The strong wind wound through the trees.
- Read:
– She loves to read novels.
– Yesterday, I read a fascinating article.
- Row:
– She planted the seeds in a row.
– There was a row about the decision.
- Polish:
– He will polish the silverware.
– She is of Polish descent.
These examples illustrate words with the same spelling or pronunciation but with different meanings, showcasing the diversity and nuances of homonyms in the English language.
You Might Also Enjoy: Top 60 Most Common Simple Sentences In English
How do you identify homonyms?

Identifying homonyms involves recognizing words that share either the same spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings. Here are steps to help you identify homonyms:
- Pay Attention to Pronunciation:
– Listen to how the word is pronounced. If two words sound the same but have different meanings, they may be homophones, a subset of homonyms.
- Look for Spelling Similarities:
– Examine words that have the same spelling but different meanings. These are homographs, another subset of homonyms.
- Consider Context:
– Evaluate the context in which the word is used. Different meanings may become apparent based on the surrounding words or the overall message.
- Check for Different Parts of Speech:
– Homonyms often manifest as words with different parts of speech. For instance, a word can be a noun in one context and a verb in another.
- Consult a Dictionary:
– If you’re unsure, consult a dictionary. Most dictionaries provide information on a word’s pronunciation, meanings, and parts of speech.
- Explore Synonyms and Antonyms:
– Investigate whether the word has synonyms or antonyms with distinct meanings. This can provide additional context for understanding the word.
- Consider Pronunciation Changes:
– In the case of homographs, where words have the same spelling but different pronunciations, be aware of shifts in sound that accompany changes in meaning.
- Note Unrelated Meanings:
– Homonyms often have meanings that are unrelated. If two meanings seem disparate, yet the words look or sound the same, they might be homonyms.
By combining attention to pronunciation, spelling, context, and the overall structure of sentences, you can effectively identify homonyms and appreciate the intricacies of the English language.

Hi, welcome to my blog! My name is Omid and I am thrilled to have you here! I am an English language teacher with 12 years of experience and hold multiple international certifications (TESOL, IELTS, TOEFL, PTE, CELTA). Additionally, I hold a PhD in Applied Linguistics with a specialization in Teaching English as a Second Language (TESL), which fuels my passion for teaching English and assisting others in mastering the language. To me, nothing is more rewarding than helping individuals enhance their English language abilities through various methods. So, let’s embark on this journey of learning English together.




